Understanding the Reordering Options in Business Central and When to Use Them

Our clients frequently ask, “Which reordering option should I use?”
Since every business is different, there is no single correct answer. But there are situations where one option is better than another.
Let’s outline Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central’s reordering options and when they are typically used in manufacturing.
ABC inventory classifications
The ABC inventory classification system is a convenient place to start:
- A items – These are typically high-cost, high-profit items. Companies generally do not keep a large inventory of A-items in stock relative to B- and C-items but want to maintain tight inventory control over them. Examples include completed high-value assemblies and subassemblies and Make-to-Order items.
- B items – Represent 20-25% of inventory. These items represent moderate value and are typically inexpensive to produce.
- C items – Represent the bulk of inventory but are of low value. Examples include nuts, bolts, table legs, etc.
Business Central provides four reordering policies to replenish inventory stock as these items run low: Order, Lot-for-Lot, Fixed Reorder Quantity, and Max Reorder Quantity.
Order reordering policy
This reordering policy is typically used for A-level items based on customer requests, such as custom jewelry or one-offs.
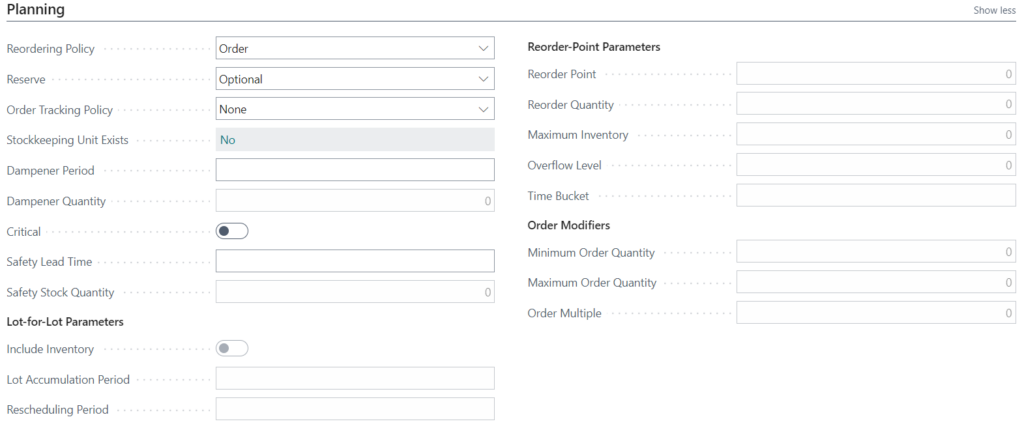
Lot-for-Lot reordering policy
Lot-for-lot is the reordering policy used most often in manufacturing and is a good default if you are unsure which reordering policy to select. Lot-for-lot typically points to B-level items. These items are ordered often and have moderate costs. For economical inventory handling, they are purchased or manufactured in a group, never one at a time. When applied to purchase orders, the lot size can be set to take advantage of discounts when ordering in bulk.
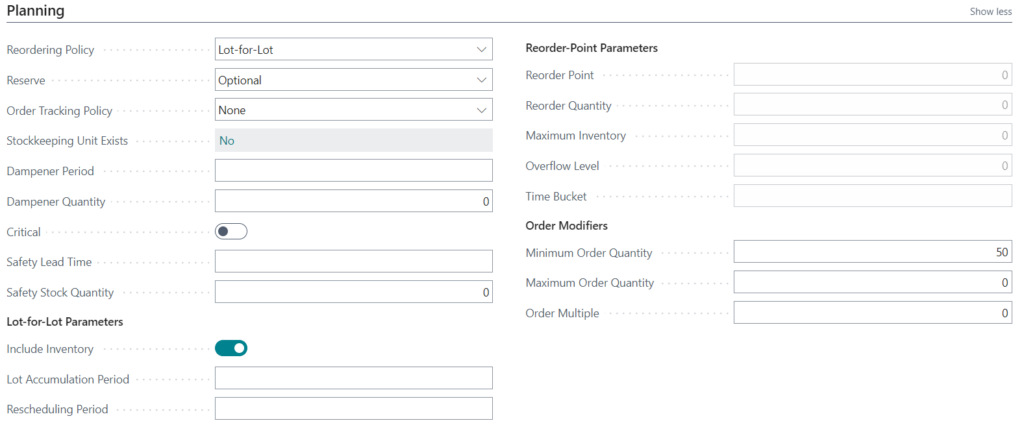
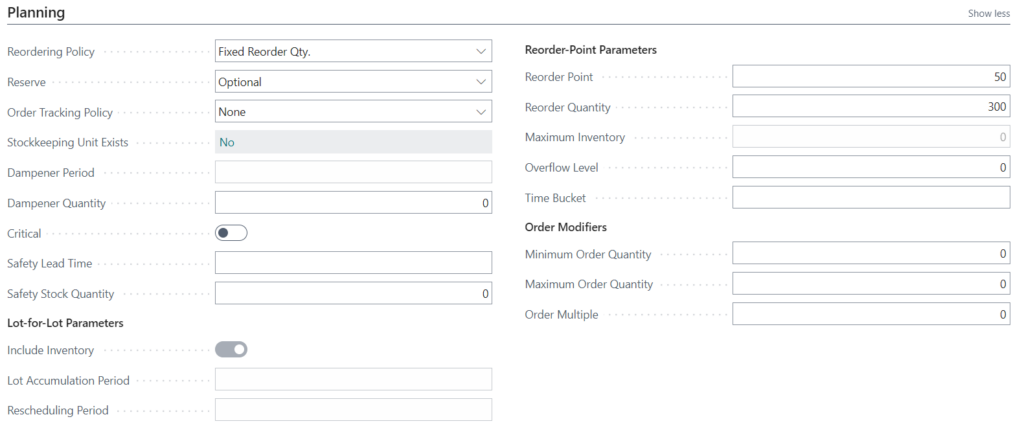
Fixed Reorder Quantity reordering policy
Fixed Reorder Quantity is often used for high-volume C-level items that you always want to have on hand and are made or purchased in large quantities. Once your inventory hits a minimum threshold, Business Central creates an order with the minimum order size. For example, once the inventory count hits 50, Business Central will generate an order to make another 300 items.
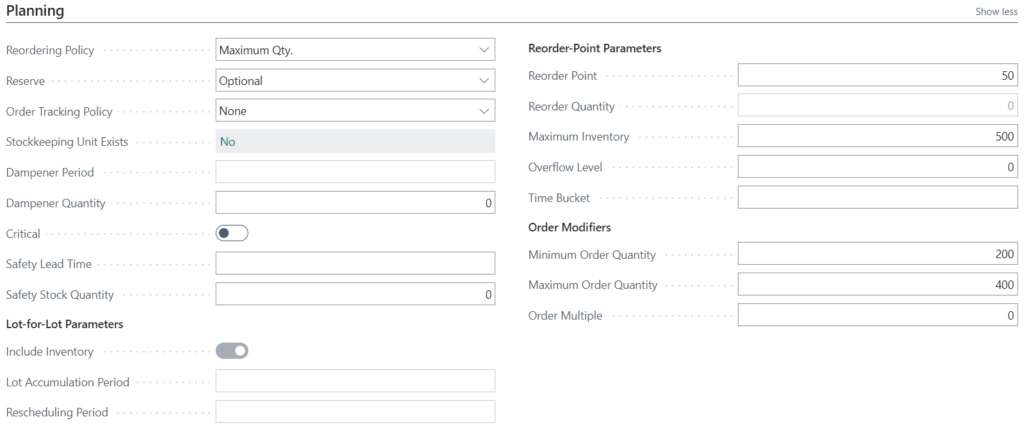
Maximum Reorder Quantity reordering policy
Maximum Reorder Quantity is similar to Fixed Order Quantity and is often used for C-level items. Here, the reorder quantity is set to a maximum value, usually due to warehouse limitations, such as warehouse space or carrying costs. Inventory is kept above the Reorder Point but less than the Maximum Inventory amount.
Contact ArcherPoint if you need help using reordering policies in Business Central.
